Abstract
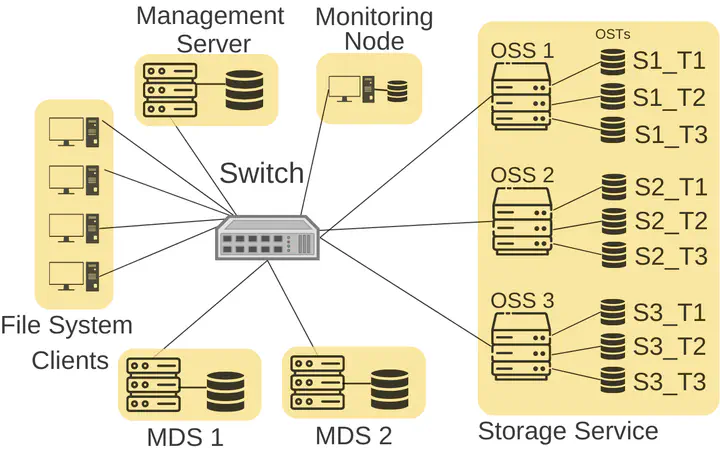
The increasing gap between processor and disk performance leads to high performance computing (HPC) applications facing I/O bottlenecks. This makes parallel file systems one of the most important components in an HPC cluster. This work analyzes the I/O performance of different workloads for various BeeGFS configurations. Our analysis shows that the default allocation strategies and striping configuration leads to an imbalanced distribution of workload data, thereby negatively affecting the I/O performance.
Type
Publication
2023 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing Workshops (CLUSTER Workshops)